Difference between revisions of "Prussia"
| [unchecked revision] | [checked revision] |
GameoAdmin (talk | contribs) (CSV import - 20130820) |
SamSteiner (talk | contribs) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:Prussiamap. | + | __TOC__ |
| − | + | [[File:Prussiamap.png|577px|thumb|right|''Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Prussiamap.png Wikipedia Commons]'']] [[File:KingdomPrussia1.jpg|285px|thumb|right|''The Kingdom of Prussia at its greatest extent (in blue), at the time of the formation of the German Empire, 1871 (in tan).<br /> | |
| − | '']] [[File:KingdomPrussia1.jpg| | + | Source: [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Main_Page Wikipedia Commons]'']] |
| − | + | [[File:FreeStatePrussia1.jpg|286px|thumb|right|''The Free State of Prussia (blue), within Germany (tan) at the time of the Weimar Republic.<br /> | |
| − | blue), at the time of the formation of the German | + | Source: [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Main_Page Wikipedia Commons]'']] |
| − | + | Prussia was an earlier designation for the territory that later became the provinces of [[East Prussia|East Prussia]] (previously Duchy of Prussia or Ducal Prussia) and [[West Prussia|West Prussia]] (previously Polish Prussia or Royal Prussia), and in 1701 the Kingdom of Prussia, ruled by the Hohenzollerns, having originated from the Electorate of [[Brandenburg (Germany)|Brandenburg]]. After [[World War (1914-1918)|World War I]] Prussia became a Free State, and after [[World War (1939-1945) - Germany|World War II]] it was dissolved. In 1914 Prussia consisted of the "old provinces" (acquired before 1866) of East Prussia, West Prussia, Pomerania, [[Poznań Voivodeship (Poland)|Posen]], Brandenburg, [[Saxony|Saxony]], [[Westphalia (Germany)|Westphalia]], and the Rhine Province, and of the "new provinces" (acquired in 1866) of [[Schleswig-Holstein (Germany)|Schleswig-Holstein]], Hanover, and Hessen-Nassau. In 1850 the principalities of Hohenzollern were added. In 1854 the principality of Neuenburg and Valengin (today the Swiss canton of [[Neuchâtel (Switzerland)|Neuchâtel]]) was given up. The rulers were [[Friedrich I, King in Prussia (1657-1713)|Friedrich I]] until 1713, [[Friedrich Wilhelm I, King in Prussia (1688-1740)|Friedrich Wilhelm I]] until 1740, [[Friedrich II, King of Prussia (1712-1786)|Friedrich II]] (the Great) until 1786, [[Friedrich Wilhelm II, King of Prussia (1744-1797)|Friedrich Wilhelm II]] until 1797, [[Friedrich Wilhelm III, King of Prussia (1770-1840)|Friedrich Wilhelm III]] until 1840, [[Friedrich Wilhelm IV, King of Prussia (1795-1861)|Friedrich Wilhelm IV]] until 1861, Wilhelm I until 1888, Friedrich III 1888, and Wilhelm II until 1918. | |
| − | Empire, 1871 (in tan). | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Source: [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Main_Page Wikipedia Commons] | ||
| − | |||
| − | '']] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | (tan) at the time of the Weimar Republic. | ||
| − | |||
| − | Source: [http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Main_Page Wikipedia Commons] | ||
| − | |||
| − | '']] | ||
In Pomerania, Posen, and Silesia there were no great numbers of Mennonites. Within the other parts of the state the various groups of Mennonites long developed in regional independence of each other, also in relation to the state. Friedrich Wilhelm I took a very different attitude toward the Mennonites in East Prussia than to the Mennonites in [[Krefeld (Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany)|Krefeld]]. Friedrich II granted specific privileges to the settlements in the [[Netzebruch (Poland)|Netzebruch]] in 1765 and to the Mennonites in the East in 1780. In 1830 Friedrich Wilhelm III, after careful preparation, issued a law particularly designed for the Mennonites in the West. But the Order of Cabinet of 1827 concerning the [[Oath|oath]] was valid for the entire state; likewise the elimination of exemption from military service of 1867, the permission granted the old Mennonite families to do noncombatant [[Military Participation|military service]], and in 1874 the law concerning the rights of the Mennonite churches to incorporate. | In Pomerania, Posen, and Silesia there were no great numbers of Mennonites. Within the other parts of the state the various groups of Mennonites long developed in regional independence of each other, also in relation to the state. Friedrich Wilhelm I took a very different attitude toward the Mennonites in East Prussia than to the Mennonites in [[Krefeld (Nordrhein-Westfalen, Germany)|Krefeld]]. Friedrich II granted specific privileges to the settlements in the [[Netzebruch (Poland)|Netzebruch]] in 1765 and to the Mennonites in the East in 1780. In 1830 Friedrich Wilhelm III, after careful preparation, issued a law particularly designed for the Mennonites in the West. But the Order of Cabinet of 1827 concerning the [[Oath|oath]] was valid for the entire state; likewise the elimination of exemption from military service of 1867, the permission granted the old Mennonite families to do noncombatant [[Military Participation|military service]], and in 1874 the law concerning the rights of the Mennonite churches to incorporate. | ||
| Line 27: | Line 10: | ||
The 1925 German census gives the following statistics (total population) for the Mennonites in Prussia: | The 1925 German census gives the following statistics (total population) for the Mennonites in Prussia: | ||
| − | <div align="center"> | + | <div align="center"> |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| − | + | | District Königsberg || align="right" | 251 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District [[Gumbinnen (Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia)|Gumbinnen]] || align="right" | 491 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Allenstein || align="right" | 40 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District West Prussia || align="right" | 3,120 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Total Province of East Prussia''' || align="right" | || align="right" | '''3,902''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | Berlin City || align="right" | 599 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Potsdam || align="right" | 144 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Frankfurt/Oder || align="right" | 74 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Total Province of Brandenburg''' || align="right" | || align="right" | '''218''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Stetten || align="right" | 40 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Köslin || align="right" | 50 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Stralsund || align="right" | 9 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Total Province of Pomerania''' || align="right" | || align="right" | '''99''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | Province of Grenzmark Posen-West Prussia || align="right" | 24 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Breslau || align="right" | 128 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Liegnitz || align="right" | 11 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Total Province of Lower Silesia''' || align="right" | || align="right" | '''139''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | Province of Upper Silesia || align="right" | 10 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Magdeburg || align="right" | 105 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Merseburg || align="right" | 62 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Erfurt || align="right" | 9 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Total Province of Saxony''' || align="right" | || align="right" | '''176''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Total Province of Schleswig-Holstein''' || align="right" | || align="right" | '''227''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Hanover || align="right" | 75 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Hildescheim || align="right" | 29 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Lüneburg || align="right" | 49 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Stade || align="right" | 24 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Osnabrück || align="right" | 34 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Aurich || align="right" | 231 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Total Province of Hanover''' || align="right" | || align="right" | '''422''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Münster || align="right" | 131 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Minden || align="right" | 16 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Arnsberg || align="right" | 159 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Total Province of Westphalia''' || align="right" | || align="right" | '''306''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Kassel || align="right" | 46 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Wiesbaden || align="right" | 89 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Total Province of Hessen-Nassau''' || align="right" | || align="right" | '''135''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Koblenz || align="right" | 66 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Düsseldorf || align="right" | 1,121 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Cologne || align="right" | 76 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Trier || align="right" | 33 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | District Aachan || align="right" | 5 || align="right" | | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Total Rhine Province''' || align="right" | || align="right" | '''1,301''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Hohenzollern''' || align="right" | || align="right" | '''21''' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | '''Grand Total''' || align="right" | || align="right" | '''7599''' | |
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | '''Cities - Mennonite Population''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Berlin || align="right" | 599 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[Königsberg (Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia)|Königsberg]] || align="right" | 78 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Stettin || align="right" | 15 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Breslau || align="right" | 74 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Magdeburg || align="right" | 38 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Halle/Saale || align="right" | 14 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Erfurt || align="right" | 6 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Kiel || align="right" | 29 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Altona || align="right" | 87 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Hanover || align="right" | 66 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Münster || align="right" | 7 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Dortmund || align="right" | 31 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Bochum || align="right" | 15 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Gelsenkirchen || align="right" | 12 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Kassel || align="right" | 20 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Frankfurt/Main || align="right" | 35 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Wiesbaden || align="right" | 47 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Essen || align="right" | 43 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Düsseldorf || align="right" | 59 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Duisburg || align="right" | 21 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Barmen || align="right" | 8 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Elberfeld || align="right" | 19 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Krefeld || align="right" | 791 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Mühlheim/Ruhr || align="right" | 8 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Hamborn || align="right" | 11 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | München/Gladbach || align="right" | 2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Oberhausen || align="right" | 32 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Cologne || align="right" | 58 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Aachen || align="right" | 2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Total'''|| align="right" | '''2,227''' | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
{{GAMEO_footer|hp=Vol. 4, pp. 224-225|date=1959|a1_last=Crous|a1_first=Ernst|a2_last=|a2_first=}} | {{GAMEO_footer|hp=Vol. 4, pp. 224-225|date=1959|a1_last=Crous|a1_first=Ernst|a2_last=|a2_first=}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Places]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:36, 24 February 2021
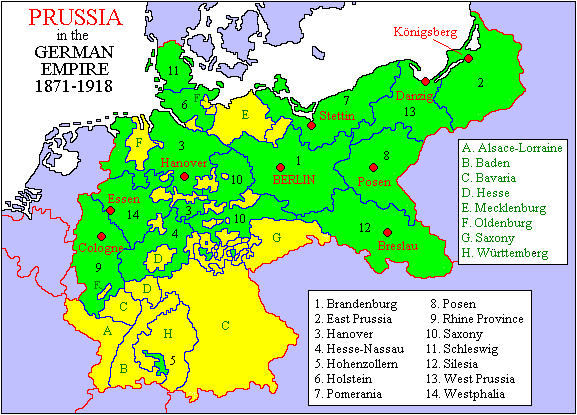
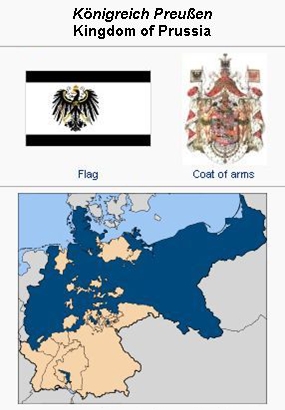
Source: Wikipedia Commons
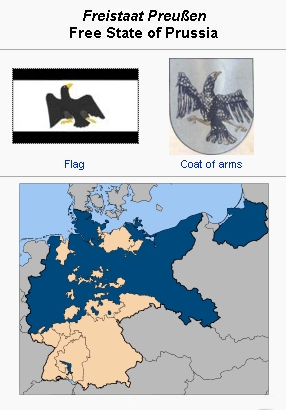
Source: Wikipedia Commons
Prussia was an earlier designation for the territory that later became the provinces of East Prussia (previously Duchy of Prussia or Ducal Prussia) and West Prussia (previously Polish Prussia or Royal Prussia), and in 1701 the Kingdom of Prussia, ruled by the Hohenzollerns, having originated from the Electorate of Brandenburg. After World War I Prussia became a Free State, and after World War II it was dissolved. In 1914 Prussia consisted of the "old provinces" (acquired before 1866) of East Prussia, West Prussia, Pomerania, Posen, Brandenburg, Saxony, Westphalia, and the Rhine Province, and of the "new provinces" (acquired in 1866) of Schleswig-Holstein, Hanover, and Hessen-Nassau. In 1850 the principalities of Hohenzollern were added. In 1854 the principality of Neuenburg and Valengin (today the Swiss canton of Neuchâtel) was given up. The rulers were Friedrich I until 1713, Friedrich Wilhelm I until 1740, Friedrich II (the Great) until 1786, Friedrich Wilhelm II until 1797, Friedrich Wilhelm III until 1840, Friedrich Wilhelm IV until 1861, Wilhelm I until 1888, Friedrich III 1888, and Wilhelm II until 1918.
In Pomerania, Posen, and Silesia there were no great numbers of Mennonites. Within the other parts of the state the various groups of Mennonites long developed in regional independence of each other, also in relation to the state. Friedrich Wilhelm I took a very different attitude toward the Mennonites in East Prussia than to the Mennonites in Krefeld. Friedrich II granted specific privileges to the settlements in the Netzebruch in 1765 and to the Mennonites in the East in 1780. In 1830 Friedrich Wilhelm III, after careful preparation, issued a law particularly designed for the Mennonites in the West. But the Order of Cabinet of 1827 concerning the oath was valid for the entire state; likewise the elimination of exemption from military service of 1867, the permission granted the old Mennonite families to do noncombatant military service, and in 1874 the law concerning the rights of the Mennonite churches to incorporate.
Additional Information
The 1925 German census gives the following statistics (total population) for the Mennonites in Prussia:
| District Königsberg | 251 | |
| District Gumbinnen | 491 | |
| District Allenstein | 40 | |
| District West Prussia | 3,120 | |
| Total Province of East Prussia | 3,902 | |
| Berlin City | 599 | |
| District Potsdam | 144 | |
| District Frankfurt/Oder | 74 | |
| Total Province of Brandenburg | 218 | |
| District Stetten | 40 | |
| District Köslin | 50 | |
| District Stralsund | 9 | |
| Total Province of Pomerania | 99 | |
| Province of Grenzmark Posen-West Prussia | 24 | |
| District Breslau | 128 | |
| District Liegnitz | 11 | |
| Total Province of Lower Silesia | 139 | |
| Province of Upper Silesia | 10 | |
| District Magdeburg | 105 | |
| District Merseburg | 62 | |
| District Erfurt | 9 | |
| Total Province of Saxony | 176 | |
| Total Province of Schleswig-Holstein | 227 | |
| District Hanover | 75 | |
| District Hildescheim | 29 | |
| District Lüneburg | 49 | |
| District Stade | 24 | |
| District Osnabrück | 34 | |
| District Aurich | 231 | |
| Total Province of Hanover | 422 | |
| District Münster | 131 | |
| District Minden | 16 | |
| District Arnsberg | 159 | |
| Total Province of Westphalia | 306 | |
| District Kassel | 46 | |
| District Wiesbaden | 89 | |
| Total Province of Hessen-Nassau | 135 | |
| District Koblenz | 66 | |
| District Düsseldorf | 1,121 | |
| District Cologne | 76 | |
| District Trier | 33 | |
| District Aachan | 5 | |
| Total Rhine Province | 1,301 | |
| Hohenzollern | 21 | |
| Grand Total | 7599 |
| Cities - Mennonite Population | |
| Berlin | 599 |
| Königsberg | 78 |
| Stettin | 15 |
| Breslau | 74 |
| Magdeburg | 38 |
| Halle/Saale | 14 |
| Erfurt | 6 |
| Kiel | 29 |
| Altona | 87 |
| Hanover | 66 |
| Münster | 7 |
| Dortmund | 31 |
| Bochum | 15 |
| Gelsenkirchen | 12 |
| Kassel | 20 |
| Frankfurt/Main | 35 |
| Wiesbaden | 47 |
| Essen | 43 |
| Düsseldorf | 59 |
| Duisburg | 21 |
| Barmen | 8 |
| Elberfeld | 19 |
| Krefeld | 791 |
| Mühlheim/Ruhr | 8 |
| Hamborn | 11 |
| München/Gladbach | 2 |
| Oberhausen | 32 |
| Cologne | 58 |
| Aachen | 2 |
| Total | 2,227 |
| Author(s) | Ernst Crous |
|---|---|
| Date Published | 1959 |
Cite This Article
MLA style
Crous, Ernst. "Prussia." Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. 1959. Web. 22 Nov 2024. https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Prussia&oldid=170125.
APA style
Crous, Ernst. (1959). Prussia. Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. Retrieved 22 November 2024, from https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Prussia&oldid=170125.
Adapted by permission of Herald Press, Harrisonburg, Virginia, from Mennonite Encyclopedia, Vol. 4, pp. 224-225. All rights reserved.
©1996-2024 by the Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. All rights reserved.
