Difference between revisions of "Ecuador"
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
m (Text replace - "Ohio (State)" to "Ohio (USA)") |
m (Rearranged images and added category.) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__FORCETOC__ | __FORCETOC__ | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
| − | [[File:Ecuador.jpg| | + | [[File:Ecuador.jpg|262px|thumb|left|''Ecuador. World Factbook, 2005 '']] |
| + | [[File:Ecuador1.jpg|247px|thumb|right|''Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Ecuador_%28orthographic_projection%29.svg Wikipedia Commons]'']] | ||
| + | == Introduction == | ||
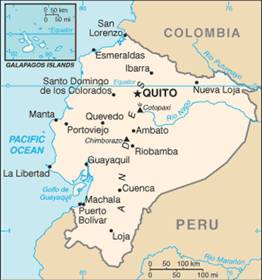
| + | The Republic of Ecuador is located in South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and by the Pacific Ocean to the west. The country also includes the Galápagos Islands in the Pacific, about 1,000 kilometers (620 mi) west of the mainland. | ||
Ecuador straddles the equator, from which it takes its name, and has an area of 283,561 km2 (109,415 square miles). Its capital city is Quito and the country's largest city is | Ecuador straddles the equator, from which it takes its name, and has an area of 283,561 km2 (109,415 square miles). Its capital city is Quito and the country's largest city is | ||
| Line 7: | Line 10: | ||
Guayaquil. In 2009 Ecuador's population was estimated at 14,573,101. In 2007 the largest ethnic group was the Mestizos (descendants of Spanish colonists and the indigenous people), constituting 65% of the population. Amerindians account for 25% of the population. The unmixed descendants of early Spanish colonists, as well as immigrants from other European countries account for about 7% of the population. Afro-Ecuadorians, including Mulattos and zambos, make up 3% of the population. | Guayaquil. In 2009 Ecuador's population was estimated at 14,573,101. In 2007 the largest ethnic group was the Mestizos (descendants of Spanish colonists and the indigenous people), constituting 65% of the population. Amerindians account for 25% of the population. The unmixed descendants of early Spanish colonists, as well as immigrants from other European countries account for about 7% of the population. Afro-Ecuadorians, including Mulattos and zambos, make up 3% of the population. | ||
| − | + | Approximately 95% of Ecuadorians are [[Roman Catholic Church|Roman Catholic]] and 4% are Protestants. In the rural parts of Ecuador, indigenous beliefs and Catholicism are sometimes syncretized. | |
| − | + | == 1990 Article == | |
| + | Elam Stauffer, a former missionary in [[Nicaragua|Nicaragua]], started the Misión Evangélica Menonita en Ecuador in 1980 in the city of Guayaquil under the auspices of the Rosedale Mennonite Missions ([[Conservative Mennonite Board of Missions and Charities|Conservative Mennonite Board of Missions and Charities]]) of [[Ohio (USA)|Ohio]]. In 1987 the [[Iglesia Evangélica Menonita Ecuatoriana|Iglesia Evangélica Menonita Ecuatoriana]] was formed. The mission also has a ministry to drug addicts and students. The mission helped flood victims in the city of Manta in 1983. As a result a congregation was born. In 1987 it had 60 members and more than 125 people attending. A preventive health program and a student center are additional ministries of the mission in Manta. | ||
The German Language Service of Radio Station HCJB, also called <em>The Voice of the Andes, </em>in Quito was begun in 1953 by Canadian missionaries David and Anne Nightingale. They were sent out and supported by the Mennonite Brethren [[Board of Foreign Missions (Mennonite Brethren Church of North America)|Board of Missions]] which staffed and supported the German service of HCJB for the first 30 years. In 1987 HCJB broadcast seven half-hour programs daily on short wave in German to Europe and the southern part of [[South America|South America]]. The content of the broadcasts is biblical, evangelistic, cultural and informative. More than 14,500 responses came from German-speaking listeners in 1986. -- <em>Sally Schroeder Isaak</em> | The German Language Service of Radio Station HCJB, also called <em>The Voice of the Andes, </em>in Quito was begun in 1953 by Canadian missionaries David and Anne Nightingale. They were sent out and supported by the Mennonite Brethren [[Board of Foreign Missions (Mennonite Brethren Church of North America)|Board of Missions]] which staffed and supported the German service of HCJB for the first 30 years. In 1987 HCJB broadcast seven half-hour programs daily on short wave in German to Europe and the southern part of [[South America|South America]]. The content of the broadcasts is biblical, evangelistic, cultural and informative. More than 14,500 responses came from German-speaking listeners in 1986. -- <em>Sally Schroeder Isaak</em> | ||
| − | + | == 2010 Update == | |
| + | In 2003 the Iglesia Evangélica Menonita Ecuatoriana had six congregations with 700 members. By 2009 the church had grown to 10 congregations with 1,050 members. | ||
= Bibliography = | = Bibliography = | ||
<em class="gameo_bibliography">Directorio de la Iglesia Evangelica del Ecuador </em>(September 1985). | <em class="gameo_bibliography">Directorio de la Iglesia Evangelica del Ecuador </em>(September 1985). | ||
| Line 25: | Line 30: | ||
Wikipedia. "Ecuador." Web. 30 October 2010. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecuador http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecuador]. | Wikipedia. "Ecuador." Web. 30 October 2010. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecuador http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecuador]. | ||
{{GAMEO_footer|hp=Vol. 5, pp. 256-257|date=October 2010|a1_last=Isaak|a1_first=Sally Schroeder|a2_last= |a2_first= }} | {{GAMEO_footer|hp=Vol. 5, pp. 256-257|date=October 2010|a1_last=Isaak|a1_first=Sally Schroeder|a2_last= |a2_first= }} | ||
| + | [[Category:Countries]] | ||
Revision as of 07:41, 20 May 2014
Introduction
The Republic of Ecuador is located in South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and by the Pacific Ocean to the west. The country also includes the Galápagos Islands in the Pacific, about 1,000 kilometers (620 mi) west of the mainland.
Ecuador straddles the equator, from which it takes its name, and has an area of 283,561 km2 (109,415 square miles). Its capital city is Quito and the country's largest city is
Guayaquil. In 2009 Ecuador's population was estimated at 14,573,101. In 2007 the largest ethnic group was the Mestizos (descendants of Spanish colonists and the indigenous people), constituting 65% of the population. Amerindians account for 25% of the population. The unmixed descendants of early Spanish colonists, as well as immigrants from other European countries account for about 7% of the population. Afro-Ecuadorians, including Mulattos and zambos, make up 3% of the population.
Approximately 95% of Ecuadorians are Roman Catholic and 4% are Protestants. In the rural parts of Ecuador, indigenous beliefs and Catholicism are sometimes syncretized.
1990 Article
Elam Stauffer, a former missionary in Nicaragua, started the Misión Evangélica Menonita en Ecuador in 1980 in the city of Guayaquil under the auspices of the Rosedale Mennonite Missions (Conservative Mennonite Board of Missions and Charities) of Ohio. In 1987 the Iglesia Evangélica Menonita Ecuatoriana was formed. The mission also has a ministry to drug addicts and students. The mission helped flood victims in the city of Manta in 1983. As a result a congregation was born. In 1987 it had 60 members and more than 125 people attending. A preventive health program and a student center are additional ministries of the mission in Manta.
The German Language Service of Radio Station HCJB, also called The Voice of the Andes, in Quito was begun in 1953 by Canadian missionaries David and Anne Nightingale. They were sent out and supported by the Mennonite Brethren Board of Missions which staffed and supported the German service of HCJB for the first 30 years. In 1987 HCJB broadcast seven half-hour programs daily on short wave in German to Europe and the southern part of South America. The content of the broadcasts is biblical, evangelistic, cultural and informative. More than 14,500 responses came from German-speaking listeners in 1986. -- Sally Schroeder Isaak
2010 Update
In 2003 the Iglesia Evangélica Menonita Ecuatoriana had six congregations with 700 members. By 2009 the church had grown to 10 congregations with 1,050 members.
Bibliography
Directorio de la Iglesia Evangelica del Ecuador (September 1985).
Material on the German HCJB Language Service is available in the Mennonite Brethren archives at the Center for Mennonite Brethren Studies, Fresno, CA.
Mennonite World Conference. "Mennonite and Brethren in Christ Churches Worldwide, 2009: Latin America & The Caribbean." 2010. Web. 28 October 2010. http://www.mwc-cmm.org/en15/files/Members 2009/Latin America & the Caribbean Summary.doc.
Mennonite World Handbook Supplement. Strasbourg, France, and Lombard, IL: Mennonite World Conference, 1984 :71.
Wikipedia. "Ecuador." Web. 30 October 2010. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ecuador.
| Author(s) | Sally Schroeder Isaak |
|---|---|
| Date Published | October 2010 |
Cite This Article
MLA style
Isaak, Sally Schroeder. "Ecuador." Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. October 2010. Web. 24 Nov 2024. https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Ecuador&oldid=122259.
APA style
Isaak, Sally Schroeder. (October 2010). Ecuador. Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. Retrieved 24 November 2024, from https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Ecuador&oldid=122259.
Adapted by permission of Herald Press, Harrisonburg, Virginia, from Mennonite Encyclopedia, Vol. 5, pp. 256-257. All rights reserved.
©1996-2024 by the Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. All rights reserved.