Difference between revisions of "Steegen (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)"
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
m |
AlfRedekopp (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "cms/ct/" to "pages/forschungshilfen/") |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
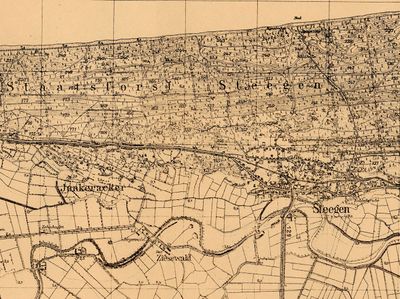
| + | [[File:Steegen1940.jpg|400px|thumbnail|left|''Detailed map of Steegen, ca. 1940.<br /> | ||
| + | Source: [http://amzpbig.com/maps/1680_Stegen_1940.jpg Archiwum Map Zachodniej Polski]''.]] | ||
[[File:Stegna.jpg|248px|thumb|right|''Source: [http://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Afbeelding:Poland_location_map.svg Wikipedia Commons]'']] | [[File:Stegna.jpg|248px|thumb|right|''Source: [http://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Afbeelding:Poland_location_map.svg Wikipedia Commons]'']] | ||
[[File:SteegenHouse.JPG|300px|thumbnail|right|''House in Steegen (now Stegna, Poland).<br /> | [[File:SteegenHouse.JPG|300px|thumbnail|right|''House in Steegen (now Stegna, Poland).<br /> | ||
Source: [http://www.ordensland.de/Landguter/landguter.html Vorlaubenhäuser im Weichselwerder, Das Land Des Deutschen Orden: Ostpreussen-Westpreussen-Memelland]''.]] | Source: [http://www.ordensland.de/Landguter/landguter.html Vorlaubenhäuser im Weichselwerder, Das Land Des Deutschen Orden: Ostpreussen-Westpreussen-Memelland]''.]] | ||
| − | Steegen (also known as Steegen-Kobbelgrube, now known as Stegna; coordinates: 54. | + | Steegen (also known as Steegen-Kobbelgrube, now known as Stegna; coordinates: 54.326389, 19.112222 [54° 19′ 35″ N, 19° 6′ 44″ E]; population in 1905, 1,240, in 2012, 4,000), a village in the Danzig Lowlands, [[West Prussia|West Prussia]], located approximately 13 kilometres (8 miles) north of Nowy Dwór Gdański ([[Tiegenhof (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)|Tiegenhof]]) and 32 km (20 mi.) east of the regional capital Gdańsk ([[Danzig, Free City of|Danzig]]). |
| + | |||
| + | Stegna was founded ca. 1300 with its privileges renewed in 1465. Initially, it was a fishing village with inns located by a route running along the sandbar and a parish church situated in Kobbelgrube and mentioned in 1465. The church in Stegna was erected in 1683 in place of an earlier one. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Until 1793 Steegen was part of Danzig in Royal Prussia (also known as Polish Prussia) in the Kingdom of [[Poland]]. The Second Partition of Poland in 1793 added Danzig and its surrounding territory to the province of [[West Prussia]]. Steegen was situated in the district (Kreis) of Danzig from 1818 until 1887, when it became part of the district of Danziger Niederung. Steegen became part of the [[Danzig, Free City of|Free City of Danzig]] from 1920 until the outbreak of World War II in 1939, when it came under the control of Nazi [[Germany]]. In February 1945 it was occupied by Soviet forces and eventually returned to Poland. In 2014 it was a village in the administrative district of Gmina Stegna, Nowy Dwór Gdański County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In 1820 Steegen had 848 inhabitants, including two that were Mennonites. Steegen is where the Mennonites regularly held meetings in 1920-45, led by a preacher of the [[Tiegenhagen (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)|Tiegenhagen]] congregation, to which the Steegen Mennonites belonged. | ||
= Bibliography = | = Bibliography = | ||
| − | "Familienforschung in Westpreußen." Hans-Jürgen Wolf. Web. 29 September 2012. http://www.westpreussen.de/ | + | "Familienforschung in Westpreußen." Hans-Jürgen Wolf. Web. 29 September 2012. http://www.westpreussen.de/pages/forschungshilfen/ortsverzeichnis/details.php?ID=6269. |
| + | |||
| + | Stowarzyszenie Konserwatorów Zabytków. "Stegna." Catalogue of Monuments of Dutch Colonization in Poland. 2005. Web. 15 September 2014. http://www.holland.org.pl/art.php?kat=obiekt&id=446&lang=en. | ||
| + | Wikipedia. "Stegna." 1 March 2013. Web. 15 September 2014. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stegna. | ||
= Maps = | = Maps = | ||
[[Map:Stegna (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)|Map:Stegna (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)]] | [[Map:Stegna (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)|Map:Stegna (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)]] | ||
| − | {{GAMEO_footer|hp=Vol. 4, p. 622|date= | + | {{GAMEO_footer|hp=Vol. 4, p. 622|date=September 2014|a1_last=Zijpp|a1_first=Nanne van der|a2_last=Thiessen|a2_first=Richard D.}} |
[[Category:Places]] | [[Category:Places]] | ||
[[Category:Cities, Towns, and Villages]] | [[Category:Cities, Towns, and Villages]] | ||
[[Category:Cities, Towns, and Villages in Poland]] | [[Category:Cities, Towns, and Villages in Poland]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:45, 23 June 2020


Source: Vorlaubenhäuser im Weichselwerder, Das Land Des Deutschen Orden: Ostpreussen-Westpreussen-Memelland.
Steegen (also known as Steegen-Kobbelgrube, now known as Stegna; coordinates: 54.326389, 19.112222 [54° 19′ 35″ N, 19° 6′ 44″ E]; population in 1905, 1,240, in 2012, 4,000), a village in the Danzig Lowlands, West Prussia, located approximately 13 kilometres (8 miles) north of Nowy Dwór Gdański (Tiegenhof) and 32 km (20 mi.) east of the regional capital Gdańsk (Danzig).
Stegna was founded ca. 1300 with its privileges renewed in 1465. Initially, it was a fishing village with inns located by a route running along the sandbar and a parish church situated in Kobbelgrube and mentioned in 1465. The church in Stegna was erected in 1683 in place of an earlier one.
Until 1793 Steegen was part of Danzig in Royal Prussia (also known as Polish Prussia) in the Kingdom of Poland. The Second Partition of Poland in 1793 added Danzig and its surrounding territory to the province of West Prussia. Steegen was situated in the district (Kreis) of Danzig from 1818 until 1887, when it became part of the district of Danziger Niederung. Steegen became part of the Free City of Danzig from 1920 until the outbreak of World War II in 1939, when it came under the control of Nazi Germany. In February 1945 it was occupied by Soviet forces and eventually returned to Poland. In 2014 it was a village in the administrative district of Gmina Stegna, Nowy Dwór Gdański County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland.
In 1820 Steegen had 848 inhabitants, including two that were Mennonites. Steegen is where the Mennonites regularly held meetings in 1920-45, led by a preacher of the Tiegenhagen congregation, to which the Steegen Mennonites belonged.
Bibliography
"Familienforschung in Westpreußen." Hans-Jürgen Wolf. Web. 29 September 2012. http://www.westpreussen.de/pages/forschungshilfen/ortsverzeichnis/details.php?ID=6269.
Stowarzyszenie Konserwatorów Zabytków. "Stegna." Catalogue of Monuments of Dutch Colonization in Poland. 2005. Web. 15 September 2014. http://www.holland.org.pl/art.php?kat=obiekt&id=446&lang=en.
Wikipedia. "Stegna." 1 March 2013. Web. 15 September 2014. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stegna.
Maps
Map:Stegna (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)
| Author(s) | Nanne van der Zijpp |
|---|---|
| Richard D. Thiessen | |
| Date Published | September 2014 |
Cite This Article
MLA style
Zijpp, Nanne van der and Richard D. Thiessen. "Steegen (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)." Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. September 2014. Web. 24 Nov 2024. https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Steegen_(Pomeranian_Voivodeship,_Poland)&oldid=168672.
APA style
Zijpp, Nanne van der and Richard D. Thiessen. (September 2014). Steegen (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland). Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. Retrieved 24 November 2024, from https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Steegen_(Pomeranian_Voivodeship,_Poland)&oldid=168672.
Adapted by permission of Herald Press, Harrisonburg, Virginia, from Mennonite Encyclopedia, Vol. 4, p. 622. All rights reserved.
©1996-2024 by the Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. All rights reserved.