Difference between revisions of "Jamaica"
| [unchecked revision] | [checked revision] |
GameoAdmin (talk | contribs) (CSV import - 20130816) |
SamSteiner (talk | contribs) (→2020 Update: updated table) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__FORCETOC__ | __FORCETOC__ | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
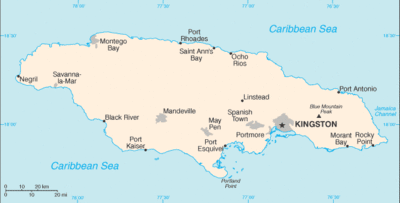
| − | + | [[File:JamaicaMap.gif|400px|thumb|left|''Jamaica. World Factbook Map, 2006 '']] | |
| + | [[File:Jamaica1.jpg|270px|thumb|right|''Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:LocationJamaica.svg Wikipedia Commons]'']] | ||
| + | == Introduction == | ||
| + | Jamaica is an island nation of the Greater Antilles, 234 kilometres (145 miles) in length and as much as 80 kilometres (50 miles) in width, amounting to 10,991 km2 (4,244 square miles). It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, about 145 kilometres (90 miles) south of Cuba, and 191 kilometres (119 miles) west of Hispaniola (Haiti and the Dominican Republic). Jamaica is the third largest island in the Caribbean. The capital city is Kingston. | ||
In July 2010 the estimated population of Jamaica was 2,847,232. Most Jamaicans are of African descent, and many are multiracial. Jamaicans of Indian and Chinese ancestry, the largest minority groups, total 160,000. | In July 2010 the estimated population of Jamaica was 2,847,232. Most Jamaicans are of African descent, and many are multiracial. Jamaicans of Indian and Chinese ancestry, the largest minority groups, total 160,000. | ||
| − | + | According to the 2001 census, the country's largest denominations are the Church of God of Prophecy (24% of the population), Seventh-day Adventist Church (11%), Pentecostal (10%), Baptist (7%), Anglican (4%), Roman Catholic (2%), United Church (2%), Methodist (2%), Jehovah's Witnesses (2%), Moravian (1%) and Plymouth Brethren (1%). The Rastafari movement had 24,020 adherents, according to the 2001 census. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Once a Spanish possession known as Santiago, Jamaica became an English colony in 1655. It achieved full independence in 1962. | Once a Spanish possession known as Santiago, Jamaica became an English colony in 1655. It achieved full independence in 1962. | ||
| − | + | == 1990 Article == | |
| + | Since 1955 the [[Jamaica Mennonite Church|Jamaica Mennonite Church]] has continued to develop. In 1957 the first church building was erected and named the Good Tidings Mennonite Church. The first annual conference convened and the church was organized with an executive committee. By 1971 the conference dispensed with the office of bishop and appointed an administrator to work for the executive committee. Pastors are appointed by the executive committee annually prior to conference meetings. Individual congregations take care of their own outreach. Pastors are receiving training at local Bible schools and colleges and refresher seminars conducted by visiting teachers from the [[United States of America|United States]]. Lay leader seminars are also conducted by national people. Its official publication is <em>The Quest. </em>The [[Virginia Mennonite Conference (Mennonite Church USA)|Virginia Mennonite Conference]] ([[Mennonite Church (MC)|Mennonite Church]]) mission board reduced its presence in the late 1970s. In 1988 there is one North American worker relating to the conference. | ||
Jamaica Mennonite Central Committee, founded in 1970, is related to [[Mennonite Central Committee (International)|Mennonite Central Committee]] (international), which sponsored Teachers Abroad Program in the 1970s and continued a presence in the country in 1988 working with other agencies in urban settings in education, social work, and medical service (nursing). [[Mennonite Economic Development Associates (MEDA)|Mennonite Economic Development Associates]] (MEDA), together with MCC, founded "Mennonite Ventures" (ca. 1986), which workrf to create employment by finding outlets for farm produce and the processing and sale of locally grown spices (1988). MCC was working closely with the Jamaica Mennonite Church and did not operate any independent projects in 1988. -- <em>Reynold Sawatzky</em> | Jamaica Mennonite Central Committee, founded in 1970, is related to [[Mennonite Central Committee (International)|Mennonite Central Committee]] (international), which sponsored Teachers Abroad Program in the 1970s and continued a presence in the country in 1988 working with other agencies in urban settings in education, social work, and medical service (nursing). [[Mennonite Economic Development Associates (MEDA)|Mennonite Economic Development Associates]] (MEDA), together with MCC, founded "Mennonite Ventures" (ca. 1986), which workrf to create employment by finding outlets for farm produce and the processing and sale of locally grown spices (1988). MCC was working closely with the Jamaica Mennonite Church and did not operate any independent projects in 1988. -- <em>Reynold Sawatzky</em> | ||
| − | + | == 2009 Update == | |
| + | [[File:ME5_736.jpg|300px|thumb|right|''Mennonite Churches in the West Indies, 1980s<br />Source: Mennonite Encyclopedia, v. 5, pp. 736-737'']] | ||
| + | In 2009 the [[Jamaica Mennonite Church]] had 13 congregations with a total membership of 704. Five of the churches are on the southwest part of the island: three on the Santa Cruz Mountain, one in the town of Santa Cruz, and one in the city of Mandeville. Four churches are located in the Kingston area and one in the city of Spanishtown. Two churches are located on the north coast in or near the town of Ocho Rios. One church is located in a mountainous area about 16 km (10 miles) outside of Montego Bay on the northwest corner of the island. | ||
| + | == 2020 Update == | ||
| + | In 2020 the following Anabaptist groups operated in Jamaica: | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto; text-align:right" | |
| − | + | ! Denominations !! Congregations<br />in 2009 !! Membership<br />in 2009 !! Congregations<br />in 2020 !! Membership<br />in 2020 | |
| − | + | |- | |
| + | | align= "left" | [[Church of God in Christ, Mennonite (CGC)|Church of God in Christ, Mennonite]] || || || 2 || 8 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align= "left" | [[Jamaica Mennonite Church]] || 13 || 675 || 13 || 704 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | align= "left" | '''Total ''' || '''13''' || '''675''' ||'''15''' || '''712''' | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | = Bibliography = | ||
| + | Horsch, James E., ed. ''Mennonite Yearbook and Directory''. Scottdale: Mennonite Publishing House (1988-89): 158. | ||
| − | + | Kraybill, Paul N., ed. ''Mennonite World Handbook''. Lombard, IL: Mennonite World Conference, 1978: 225-226. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | Mennonite World Conference. "Global Map: Jamaica." Mennonite World Conference. Web. 1 April 2021. <nowiki>https://mwc-cmm.org/global-map</nowiki>. | |
| − | Mennonite World Conference. "Mennonite and Brethren in Christ Churches Worldwide, 2009: Latin America & The Caribbean." 2010. Web. 28 October 2010. | + | Mennonite World Conference. "Mennonite and Brethren in Christ Churches Worldwide, 2009: Latin America & The Caribbean." 2010. Web. 28 October 2010. [broken link]. |
| − | Mennonite World Conference. "MWC - 2003 Caribbean, Central & South America Mennonite & Brethren in Christ Churches." Web. 9 March 2006. [ | + | Mennonite World Conference. "MWC - 2003 Caribbean, Central & South America Mennonite & Brethren in Christ Churches." Web. 9 March 2006. [broken link]. |
| − | + | ''Mennonite World Handbook Supplement''. Strasbourg, France, and Lombard, IL: Mennonite World Conference, 1984 :82. | |
Wikipedia. "Jamaica." Web. 31 October 2010. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jamaica http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jamaica]. | Wikipedia. "Jamaica." Web. 31 October 2010. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jamaica http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jamaica]. | ||
| − | + | {{GAMEO_footer|hp=Vol. 5, p. 459|date=April 2020|a1_last=Sawatzky|a1_first=Reynold|a2_last= |a2_first= }} | |
| − | + | [[Category:Countries]] | |
| − | {{GAMEO_footer|hp=Vol. 5, p. 459|date= | ||
Latest revision as of 15:10, 1 April 2021
Introduction
Jamaica is an island nation of the Greater Antilles, 234 kilometres (145 miles) in length and as much as 80 kilometres (50 miles) in width, amounting to 10,991 km2 (4,244 square miles). It is situated in the Caribbean Sea, about 145 kilometres (90 miles) south of Cuba, and 191 kilometres (119 miles) west of Hispaniola (Haiti and the Dominican Republic). Jamaica is the third largest island in the Caribbean. The capital city is Kingston.
In July 2010 the estimated population of Jamaica was 2,847,232. Most Jamaicans are of African descent, and many are multiracial. Jamaicans of Indian and Chinese ancestry, the largest minority groups, total 160,000.
According to the 2001 census, the country's largest denominations are the Church of God of Prophecy (24% of the population), Seventh-day Adventist Church (11%), Pentecostal (10%), Baptist (7%), Anglican (4%), Roman Catholic (2%), United Church (2%), Methodist (2%), Jehovah's Witnesses (2%), Moravian (1%) and Plymouth Brethren (1%). The Rastafari movement had 24,020 adherents, according to the 2001 census.
Once a Spanish possession known as Santiago, Jamaica became an English colony in 1655. It achieved full independence in 1962.
1990 Article
Since 1955 the Jamaica Mennonite Church has continued to develop. In 1957 the first church building was erected and named the Good Tidings Mennonite Church. The first annual conference convened and the church was organized with an executive committee. By 1971 the conference dispensed with the office of bishop and appointed an administrator to work for the executive committee. Pastors are appointed by the executive committee annually prior to conference meetings. Individual congregations take care of their own outreach. Pastors are receiving training at local Bible schools and colleges and refresher seminars conducted by visiting teachers from the United States. Lay leader seminars are also conducted by national people. Its official publication is The Quest. The Virginia Mennonite Conference (Mennonite Church) mission board reduced its presence in the late 1970s. In 1988 there is one North American worker relating to the conference.
Jamaica Mennonite Central Committee, founded in 1970, is related to Mennonite Central Committee (international), which sponsored Teachers Abroad Program in the 1970s and continued a presence in the country in 1988 working with other agencies in urban settings in education, social work, and medical service (nursing). Mennonite Economic Development Associates (MEDA), together with MCC, founded "Mennonite Ventures" (ca. 1986), which workrf to create employment by finding outlets for farm produce and the processing and sale of locally grown spices (1988). MCC was working closely with the Jamaica Mennonite Church and did not operate any independent projects in 1988. -- Reynold Sawatzky
2009 Update
In 2009 the Jamaica Mennonite Church had 13 congregations with a total membership of 704. Five of the churches are on the southwest part of the island: three on the Santa Cruz Mountain, one in the town of Santa Cruz, and one in the city of Mandeville. Four churches are located in the Kingston area and one in the city of Spanishtown. Two churches are located on the north coast in or near the town of Ocho Rios. One church is located in a mountainous area about 16 km (10 miles) outside of Montego Bay on the northwest corner of the island.
2020 Update
In 2020 the following Anabaptist groups operated in Jamaica:
| Denominations | Congregations in 2009 |
Membership in 2009 |
Congregations in 2020 |
Membership in 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Church of God in Christ, Mennonite | 2 | 8 | ||
| Jamaica Mennonite Church | 13 | 675 | 13 | 704 |
| Total | 13 | 675 | 15 | 712 |
Bibliography
Horsch, James E., ed. Mennonite Yearbook and Directory. Scottdale: Mennonite Publishing House (1988-89): 158.
Kraybill, Paul N., ed. Mennonite World Handbook. Lombard, IL: Mennonite World Conference, 1978: 225-226.
Mennonite World Conference. "Global Map: Jamaica." Mennonite World Conference. Web. 1 April 2021. https://mwc-cmm.org/global-map.
Mennonite World Conference. "Mennonite and Brethren in Christ Churches Worldwide, 2009: Latin America & The Caribbean." 2010. Web. 28 October 2010. [broken link].
Mennonite World Conference. "MWC - 2003 Caribbean, Central & South America Mennonite & Brethren in Christ Churches." Web. 9 March 2006. [broken link].
Mennonite World Handbook Supplement. Strasbourg, France, and Lombard, IL: Mennonite World Conference, 1984 :82.
Wikipedia. "Jamaica." Web. 31 October 2010. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jamaica.
| Author(s) | Reynold Sawatzky |
|---|---|
| Date Published | April 2020 |
Cite This Article
MLA style
Sawatzky, Reynold. "Jamaica." Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. April 2020. Web. 12 Feb 2026. https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Jamaica&oldid=171052.
APA style
Sawatzky, Reynold. (April 2020). Jamaica. Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. Retrieved 12 February 2026, from https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Jamaica&oldid=171052.
Adapted by permission of Herald Press, Harrisonburg, Virginia, from Mennonite Encyclopedia, Vol. 5, p. 459. All rights reserved.
©1996-2026 by the Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. All rights reserved.