Difference between revisions of "Schönhorst (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)"
| [unchecked revision] | [checked revision] |
GameoAdmin (talk | contribs) (CSV import - 20130816) |
m (Added categories and added image.) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
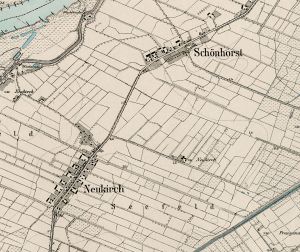
| − | + | [[File:Schoenhorst-Neukirch.jpg|300px|thumbnail|left|''Detailed map of Schönhorst and Neukirch. <br /> | |
| − | + | Source: [http://amzpbig.com/maps/1879_Gr_Lichtenau_1909.jpg Archiwum Map Zachodniej Polski]''.]] | |
| − | Source: [http:// | + | [[File:Schoenhorst.jpg|300px|thumb|right|''Schönhorst (now Gniazdowo, Poland)<br /> |
| − | + | Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gniazdowo,_Pomeranian_Voivodeship Wikipedia Commons]'']] | |
| − | + | [[File:Schoenhorst%20house.jpg|300px|thumb|right|''Schönhorst house from 1760<br /> | |
| − | + | Source: [http://holland.org.pl/art.php Catalogue of Monuments of Dutch Colonization in Poland website]'']] | |
| − | '']] | + | Schönhorst (Schoenhorst; now known as Gniazdowo; coordinates: 54.19383, 18.924722 [54° 11′ 37″ N, 18° 55′ 28″ E]; population in 1905, 410; population in 2012, 262), is located approximately 4 kilometres (2 miles) south-west of Ostaszewo, 13 km (8 mi.) west of Nowy Dwór Gdański ([[Tiegenhof (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)|Tiegenhof]]), and 27 km (17 mi.) south-east of the regional capital Gdańsk ([[Danzig (Poland)|Danzig]]). |
| − | |||
| − | Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gniazdowo,_Pomeranian_Voivodeship Wikipedia Commons] | ||
| − | |||
| − | '']] | ||
Schönhorst was first mentioned in historical documents in 1333 and received Chełmno rights (Kulm Law, a legal constitution for a municipal form of government) in 1349 from Heinrich Dusemer von Arfberg, the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights. Until 1772 Schönhorst was part of the Kingdom of [[Poland|Poland]]. The First Partition of Poland in 1772 resulted in the creation of a new province in 1773, called [[West Prussia|West Prussia]], in which Schönhorst was located. Schönhorst was situated in the district (Kreis) of Marienburg until the establishment of the [[Danzig, Free City of|Free City of Danzig]] in 1920. The village came under the control of Nazi Germany during World War II until February 1945, when it was occupied by Soviet forces and returned to Poland. In 2012 Schönhorst (now Gniazdowo) was a village in the administrative district of Gmina Ostaszewo, within Nowy Dwór Gdański County, Pomeranian Voivodeship. | Schönhorst was first mentioned in historical documents in 1333 and received Chełmno rights (Kulm Law, a legal constitution for a municipal form of government) in 1349 from Heinrich Dusemer von Arfberg, the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights. Until 1772 Schönhorst was part of the Kingdom of [[Poland|Poland]]. The First Partition of Poland in 1772 resulted in the creation of a new province in 1773, called [[West Prussia|West Prussia]], in which Schönhorst was located. Schönhorst was situated in the district (Kreis) of Marienburg until the establishment of the [[Danzig, Free City of|Free City of Danzig]] in 1920. The village came under the control of Nazi Germany during World War II until February 1945, when it was occupied by Soviet forces and returned to Poland. In 2012 Schönhorst (now Gniazdowo) was a village in the administrative district of Gmina Ostaszewo, within Nowy Dwór Gdański County, Pomeranian Voivodeship. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 12: | ||
The [[Flemish Mennonites|Flemish Mennonites]] of Schönhorst, who comprised the majority of Mennonites in Schönhorst in the late 18th century, were members of the [[Ladekopp (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)|Ladekopp]] Mennonite Church while the minority [[Frisian Mennonites|Frisian Mennonites]] were members of the [[Orlofferfelde (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)|Orlofferfelde]] Mennonite Church. | The [[Flemish Mennonites|Flemish Mennonites]] of Schönhorst, who comprised the majority of Mennonites in Schönhorst in the late 18th century, were members of the [[Ladekopp (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)|Ladekopp]] Mennonite Church while the minority [[Frisian Mennonites|Frisian Mennonites]] were members of the [[Orlofferfelde (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)|Orlofferfelde]] Mennonite Church. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= Bibliography = | = Bibliography = | ||
Stowarzyszenie Konserwatorów Zabytków. "Gniazdowo." Catalogue of Monuments of Dutch Colonization in Poland. 2005. Web. 18 October 2012. [http://holland.org.pl/art.php http://holland.org.pl/art.php?kat=obiekt&id=324&lang=en]. | Stowarzyszenie Konserwatorów Zabytków. "Gniazdowo." Catalogue of Monuments of Dutch Colonization in Poland. 2005. Web. 18 October 2012. [http://holland.org.pl/art.php http://holland.org.pl/art.php?kat=obiekt&id=324&lang=en]. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 18: | ||
Wolf, Hans-Jürgen. "Familienforschung in Westpreußen." Web. 18 October 2012. [http://www.westpreussen.de/cms/ct/ortsverzeichnis/details.php http://www.westpreussen.de/cms/ct/ortsverzeichnis/details.php?ID=5930]. | Wolf, Hans-Jürgen. "Familienforschung in Westpreußen." Web. 18 October 2012. [http://www.westpreussen.de/cms/ct/ortsverzeichnis/details.php http://www.westpreussen.de/cms/ct/ortsverzeichnis/details.php?ID=5930]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= Maps = | = Maps = | ||
[[Map:Gniazdowo (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)|Map:Gniazdowo (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)]] | [[Map:Gniazdowo (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)|Map:Gniazdowo (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)]] | ||
{{GAMEO_footer|hp=|date=October 2012|a1_last=Thiessen|a1_first=Richard D|a2_last=|a2_first=}} | {{GAMEO_footer|hp=|date=October 2012|a1_last=Thiessen|a1_first=Richard D|a2_last=|a2_first=}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Cities, Towns, and Villages]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Cities, Towns, and Villages in Poland]] | ||
Revision as of 07:10, 11 August 2014
Schönhorst (Schoenhorst; now known as Gniazdowo; coordinates: 54.19383, 18.924722 [54° 11′ 37″ N, 18° 55′ 28″ E]; population in 1905, 410; population in 2012, 262), is located approximately 4 kilometres (2 miles) south-west of Ostaszewo, 13 km (8 mi.) west of Nowy Dwór Gdański (Tiegenhof), and 27 km (17 mi.) south-east of the regional capital Gdańsk (Danzig).
Schönhorst was first mentioned in historical documents in 1333 and received Chełmno rights (Kulm Law, a legal constitution for a municipal form of government) in 1349 from Heinrich Dusemer von Arfberg, the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights. Until 1772 Schönhorst was part of the Kingdom of Poland. The First Partition of Poland in 1772 resulted in the creation of a new province in 1773, called West Prussia, in which Schönhorst was located. Schönhorst was situated in the district (Kreis) of Marienburg until the establishment of the Free City of Danzig in 1920. The village came under the control of Nazi Germany during World War II until February 1945, when it was occupied by Soviet forces and returned to Poland. In 2012 Schönhorst (now Gniazdowo) was a village in the administrative district of Gmina Ostaszewo, within Nowy Dwór Gdański County, Pomeranian Voivodeship.
In 1772, farms belonged to 8 Mennonites and 4 other owners. The Prussian census of 1776 lists ten Mennonite families in Schönhorst with the following surnames: Dau, Dick, Epp, Fast, Harder, Penner, Regehr, and Wiebe. In 1820, the village had 294 residents, including 43 Mennonites. In 1885, the village had 442 residents, including 45 Mennonites.
The Flemish Mennonites of Schönhorst, who comprised the majority of Mennonites in Schönhorst in the late 18th century, were members of the Ladekopp Mennonite Church while the minority Frisian Mennonites were members of the Orlofferfelde Mennonite Church.
Bibliography
Stowarzyszenie Konserwatorów Zabytków. "Gniazdowo." Catalogue of Monuments of Dutch Colonization in Poland. 2005. Web. 18 October 2012. http://holland.org.pl/art.php?kat=obiekt&id=324&lang=en.
Wikipedia. "Gniazdowo, Pomeranian Voivodeship." Web. 18 October 2012. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gniazdowo,_Pomeranian_Voivodeship.
Wolf, Hans-Jürgen. "Familienforschung in Westpreußen." Web. 18 October 2012. http://www.westpreussen.de/cms/ct/ortsverzeichnis/details.php?ID=5930.
Maps
Map:Gniazdowo (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)
| Author(s) | Richard D Thiessen |
|---|---|
| Date Published | October 2012 |
Cite This Article
MLA style
Thiessen, Richard D. "Schönhorst (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland)." Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. October 2012. Web. 16 Apr 2024. https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Sch%C3%B6nhorst_(Pomeranian_Voivodeship,_Poland)&oldid=124006.
APA style
Thiessen, Richard D. (October 2012). Schönhorst (Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland). Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. Retrieved 16 April 2024, from https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Sch%C3%B6nhorst_(Pomeranian_Voivodeship,_Poland)&oldid=124006.
©1996-2024 by the Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. All rights reserved.